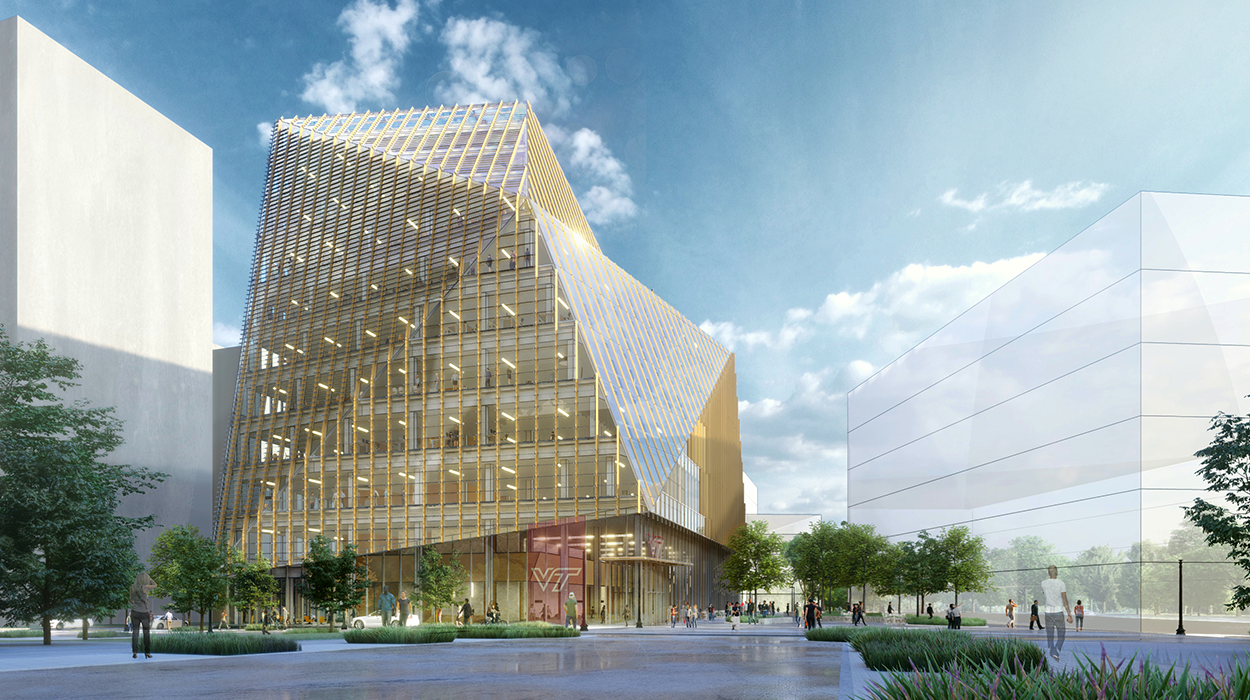
Virginia Tech Innovation Campus rendering, Alexandria
Virginia Tech: Innovation Leader
Virginia Tech's $1 billion, 1 million-square-foot graduate Innovation Campus focused on technology positions the university and its future partners near the nation's capital, diverse industries, and leading tech companies, including Amazon HQ2. Research at the Innovation Campus will emphasize quantum information sciences, intelligent interfaces, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. Virginia Tech's Chip-Scale Integration program is one of 14 specialized majors in electrical engineering and computer engineering.